For Women: 7 reasons to appreciate excess body hair more
What you need to know about hair growth in unwanted places like face, arms, legs, chest, back, and appropriate treatment.
There are three reasons to love hairy body:
It is a way your body tells you that it is going through something.
It is genetics.
It is beautiful.
Even when you want to get rid of it, you have to identify the issue before you get the razor out!
1. It’s in your family
Genetics play a major part in hairy bodie. Some ethnic groups, darker-skinned people usually have excessive hair.
Unfortunately, the most reliable way to get rid of hair on dark-skin affects melanin.
The laser targets melanin in the hair. But this includes melanin of the skin which can leave you covered in permanent white patches allover if done incorrectly.
2. It fights back
If you are going to cut it, make sure to leave nothing behind. But even then, there’s a chance you are only making it stronger.
Shaving cut the hair but doesn’t impact the hair pocket (follicle). Even invasive methods like waxing and tweezing can make it come back thicker and coarser.
The injury to the hair makes it respond by becoming thicker than the previously cut batch.
The solution is to get a cream that can slow down the growth rate between shaving, waxing or tweezing.
3. You have sensitive follicles
If a medical practitioner has ruled out medical causes, you might simply have sensitive follicles.
This means they overreact to even normal testosterone levels.
Medical conditions the excess hair might be telling you about
4. Hormone imbalance
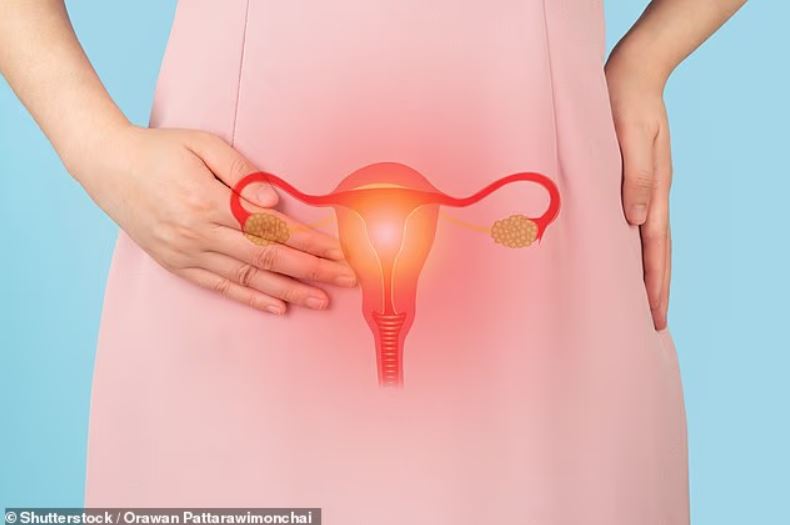
“Women with polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) usually have excessive growth of facial or body hair because the condition produces excessive amounts of androgens (excessive male sex hormones),” says Ghasak Amer Mahmood, MD, an endocrinologist at PIH Health in Whittier, California.
Treatment includes medicine to regulate ovaries function and decrease amount of androgens. These include: birth control pills and anti-androgen medicine.
5. Adrenal gland issues
“In Cushing’s syndrome, the major product of the adrenal gland, cortisol, is increased, but along with it, excess androgens are released as well. In congenital adrenal hyperplasia, there is a deficiency in one of the enzymes that produce cortisol.
As a result, cortisol can’t be produced, and the precursors are diverted to producing androgens instead, leading to excessive hair growth,” says Mazen Abdallah, MD, a reproductive endocrinologist with McGovern Medical School at UT Health and Children’s Memorial Hermann Hospital, and medical director of the Houston Fertility Institute in Texas.
Surgery or medication should be able to restore normal levels.
6. Weight gain
Extra weight is linked to high levels of male hormones.
“Obesity alters the way that the body produces and processes hormones,” Dr. Ward explains. “When insulin levels in the body are high they stimulate the production of male hormones.
This is also linked to PCOS and diabetes, a condition that also affects insulin levels,” the doctor adds.
Lifestyle changes including a diet low in sugar and fat and rich in antioxidants, and weight loss can lessen hair growth.
7. Medication
Treatment for endometriosis (a disease characterized by the presence of tissue resembling endometrium (the lining of the uterus) outside the uterus) can lead to excess hair growth.
It includes steroids like prednisone, danazol, which are created from androgens. Medicine for immune disorders or anti-seizure and drugs used to slow hair loss may cause hair in unwanted places.